Indus Water Treaty 1960.
- Indus Waters Treaty was signed in 1960, between India and Pakistan and brokered by the World Bank.
- The treaty fixed and delimited the rights and obligations of both countries concerning the use of the waters of the Indus River system.
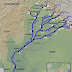
- The Treaty deals with sharing of water of six rivers i.e. Indus, Chenab, Jhelum, Beas, Ravi and Sutlej between India and Pakistan.
- The treaty gave India “unrestricted use” of the eastern rivers, the Sutlej, Ravi and Beas. While, Pakistan had unrestricted use of the western rivers, the Chenab, Jhelum and Indus.
- On the main river Indus too, India was given the right to exploit without disturbing the flow or quantum.
- The treaty also granted India the use of the western rivers for domestic, agricultural and non-consumptive uses including power production, but it must do so in accordance with the provisions of the Treaty.
- As per the treaty, the water commissioners of Pakistan and India are required to meet twice a year and arrange technical visits to project sites and critical river head works.
- Both the sides share details of the water flow and the quantum of water being used under the treaty.
- The treaty sets out a mechanism for cooperation and information exchange between the two countries regarding their use of the rivers.

Pakistan's dependence over the Indus river system
- Indus basin has more than 95% of Pakistan’s irrigation infrastructure
- It has now become the world’s largest contiguous irrigation system, comprising over 60,000 km of canals.
- Three of Pakistan’s biggest dams (including world's largest dam- Mangla dam) is built on the Jhelum river, producing a substantial proportion of Pakistan’s electricity.
Projects to exploit unused river water of eastern rivers: Water of eastern rivers will be diverted to Yamuna through the following three projects:
- Ujh Dam in Jammu and Kashmir
- Shahapur Kandi Project on the Ravi
- Second Ravi-Beas link
Pakistan's objections over Indian Projects: Even before India’s shift in policy, Pakistan had often blamed India for violating the provisions of the Indus Waters Treaty.
Examples include
- Ratle hydroelectric project on the Chenab
- Pakal Dul dam on Marusadar River (a tributary of the Chenab River)
- Sawalkot project on the Chenab
- Kishenganga project on the Jhelum








No comments
Welcome to the world of the seekers